Topographical Map
Topographical Map (Toposheet)
Topographical map with surface contours prepared and published by Survey of India.It is the excellent base map for geological mapping. A topographical map shows the surface features (mountains, hills, valleys, rivers, canals, lakes, swamps, wells, roads, railways, vegetation, villages, towns etc.) on a sufficiently large scale to enable the individual features to be identified on the ground by their shape and position. The scale of Indian Toposheet is 1:50000.
Symbols/Legend/Key
Symbols are used to represent topographic features on the map. Every map contains a symbol. Symbols are lines, polygon, points, arrow, alphabets, colours, shadings to represent different features.
Point symbol
It represents the location and entity or other characteristic feature of a small territorial extent to the map scale. It depends on the scale of a map. When a map is prepared on 1:1000000 scale a village may be represented as a point but on 1:10000 it can be represented on polygon.
Line Symbol
It is used to represent linear features such as roads, railway lines, contour, grid lines.
Polygon symbol
It is used to represent aerial extent in relation to map scale.
Arrow symbol
The arrow pointing upward in the map showing north direction. North is also regarded as zero direction or base direction line.
Relief feature
It is important feature without which one can not have the true idea of the terrain from the map. Relief is represented with the help of layering, shading, hatchuring, contouring etc.
Significance of Colours in topographical map -
Blue
All water bodies containing water are represented in Blue colour.
Green
All vegetation or forest area are represented in green colour.
Black
All names, river banks, broken ground, dry streams, height and their numbering, railway lines, surveyed trees, telephone and telegraph lines, lines of longitudes and latitudes.
White patches
It represents uncultivated lands.
Yellow patches
It represents all cultivated areas.
Brown
It represents contour lines their numberings, sand features like sand dunes and sand hills.
Red
Grid lines ( easting and nothing) and their numbering, roads, cart tracks, settlement, hut and buildings.
Calculation area
In the Toposheet map 1cm =500m
Hence 2cm= 1Km.
Area = Length x Breadth
Area of each grid on the map
= 2cm x 2cm
= 4 sqcm on map
= 1km x 1km
1km2 on the ground.
It can also be expressed as
Area of each square = 4 sqcm
1000 x 1000
or. 1000000 sqm.
The area of a Toposheet is about 729 sqkm
Numbering of Toposheet
India comprises of 39 -92 (54) million sheets. In the IAC series each million sheet is bounded by 4° Latitude and 4° Longitude. The numbering starts from 40° North Latitude and 44° Longitude. The number increases from North to South as shown in fig below. The sheets falling in sea are not numbered. The scale of each million sheet is 1:1000000.
Each million sheet is further subdivided into 16 equal degree sheets. Each degree sheet is bounded by 1° Latitude and 1° Longitude. The scale of degree sheet is 1:250000. The numbering of degree sheet are arranged in the following manner.
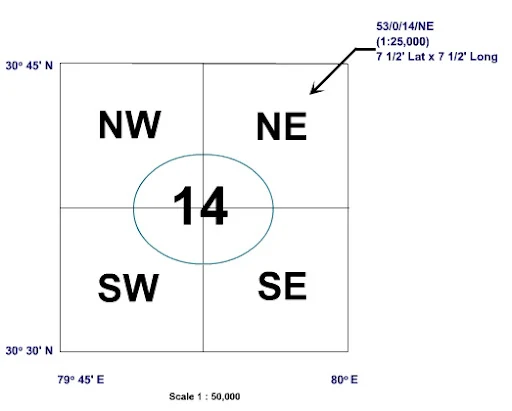
Each degree sheet is further subdivided into 16 Toposheets. Each Toposheet is bounded by 15' Latitude and 15' Longitude. The scale of the Toposheet is 1:50000. Each Toposheet is further subdivided into 4 quadrants like NE, SE, SW and NW quadrants as shown in fig below.
Solve the following questions-
1. The scale of Indian Toposheet is
a) 1:100000 b) 1:20000
c) 1:50000. d) 1:500000
2. The scale of a degree sheet is
a)1:25000. b) 1:250000
c) 1:50000 d). 1:1000000
3. The side of a million sheet comprises of
a) 4°. b) 2°
c) 1°. d) 15'
4. India comprises of million sheet from
a) 39-92 b) 29-62
c) 52-92 d) None of the above.
5. Contour in the Toposheet is represented by
a) White colour b) Black colour
c) Brown colour d) Red colour.









1 c
ReplyDelete2 d
3 a
4 a
5 a
5 c
Delete1 d 2b 3a 4a 5c
ReplyDelete1 - (c)
ReplyDelete2 - (d)
3 - (a)
4 - (a)
5 - (c)