Classification of Mineral deposits
An ore deposit is an volume of rock enriched in one or more minerals of economic importance.
Classification of ore deposits on the basis of genesis and mode of occurrences are mainly -
1. Magmatic ore deposits
2. Hydrothermal ore deposits
3. Sedimentary ore deposits
4. Supergene sulphide enrichment
5. Metamorphic ore deposits
1. Magmatic ore deposits
These are generated through the process of magmatic intrusions. The economic minerals accumulate to form magmatic ore deposits.
It is further subdivided into -
i) Magmatic segregation
Fractional crystallization of cooling magic magma leading to development of oxides and silicates. Segregation is a general term refering to any process by which one or more minerals become locally concentrated during cooling and crystallization of magma. Eg. Pt, Fe, Ni, Cr, Ti, V deposits.
ii) Pegmatitic deposits
These deposits generally occur in association with granites. Pegmatites are very large single crystals. Eg. Mica formed when magma migtrated into fractures due to very low viscosity and cool very slowly.
iii) Porphyry ore deposits
These are formed at depth under island arcs. Large crystals form slowly, then iron rich melt escapes and cools quickly in small cracks leaving veins of ores.
E.g. Porphyry Cu ore deposit.
2. Hydrothermal ore deposits
Hydrothermal deposits are produced from ground water circulates down to depths and heats up either by coming near to hot igneous or by circulating to great depth which naturally heat the water due to geothermal gradient. Such hot water can dissolve valuable minerals sa it passes through a large volume of rock. As the hot water moves into cooler areas of the crust, dissolved substances are precipitated from the hot water solution.
3. Sedimentary ore deposits
These are typically produced by chemical deposition.
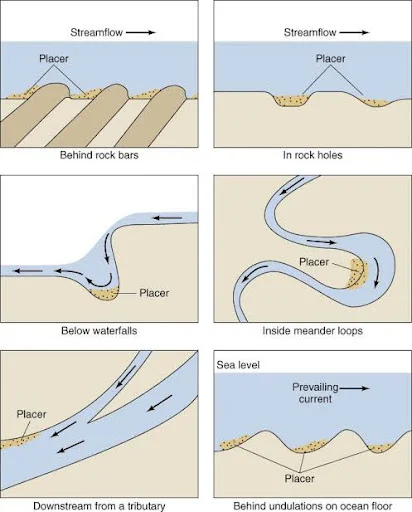
Placer deposits
Residual ore deposits
4. Supergene sulphide enrichment
It s the natural upgradation of pre-existing buried sulphide deposit.














Comments
Post a Comment